Build In Script
The Built-In Script system provides pre-configured diagnostic services for common UDS operations. This documentation covers the available built-in scripts and their functionality.
Supported Built-In Script
SecureAccessGenerateKeyEx
This script is used to generate a key for the security access process. see GenerateKeyEx.
VKeyGenResultEx GenerateKeyEx (
const unsigned char* ipSeedArray,
unsigned int iSeedArraySize,
const unsigned int iSecurityLevel,
const char* ipVariant,
unsigned char* iopKeyArray,
unsigned int iMaxKeyArraySize,
unsigned int& oActualKeyArraySize
);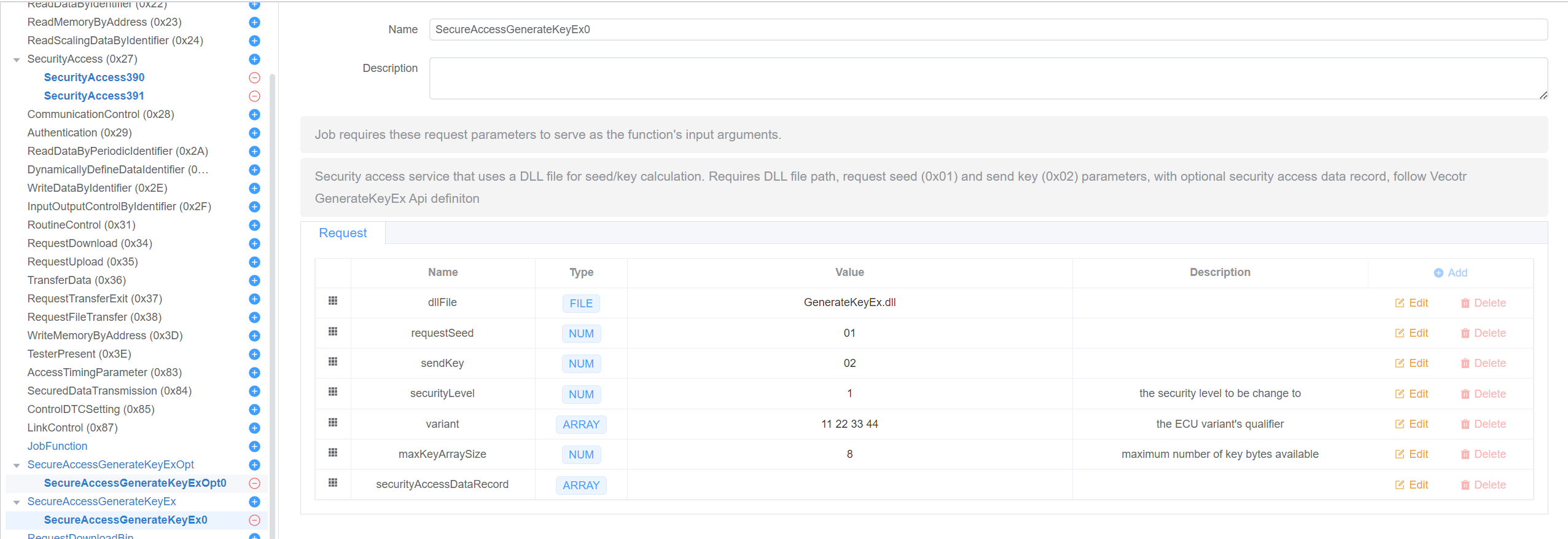
Parameters
- dllFile
- The path to the DLL file, the DLL must be a 64-bit DLL file and contains the GenerateKeyEx function.
VKeyGenResultEx GenerateKeyEx (
const unsigned char* ipSeedArray,
unsigned int iSeedArraySize,
const unsigned int iSecurityLevel,
const char* ipVariant,
unsigned char* iopKeyArray,
unsigned int iMaxKeyArraySize,
unsigned int& oActualKeyArraySize
);requestSeed
- The request seed sub-function, 1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15
- Default: 0x01
sendKey
- The send key sub-function, 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16
- Default: 0x02
securityLevel
- The security level to be change to
variant
- The variant of the security access process
maxKeyArraySize
- The max key array size
securityAccessDataRecord
- The security access data record in request seed DiagRequest, the data will be sent to the ECU in the request seed sub-function.
SecureAccessGenerateKeyExOpt
This script is used to generate a key for the security access process. see GenerateKeyExOpt.
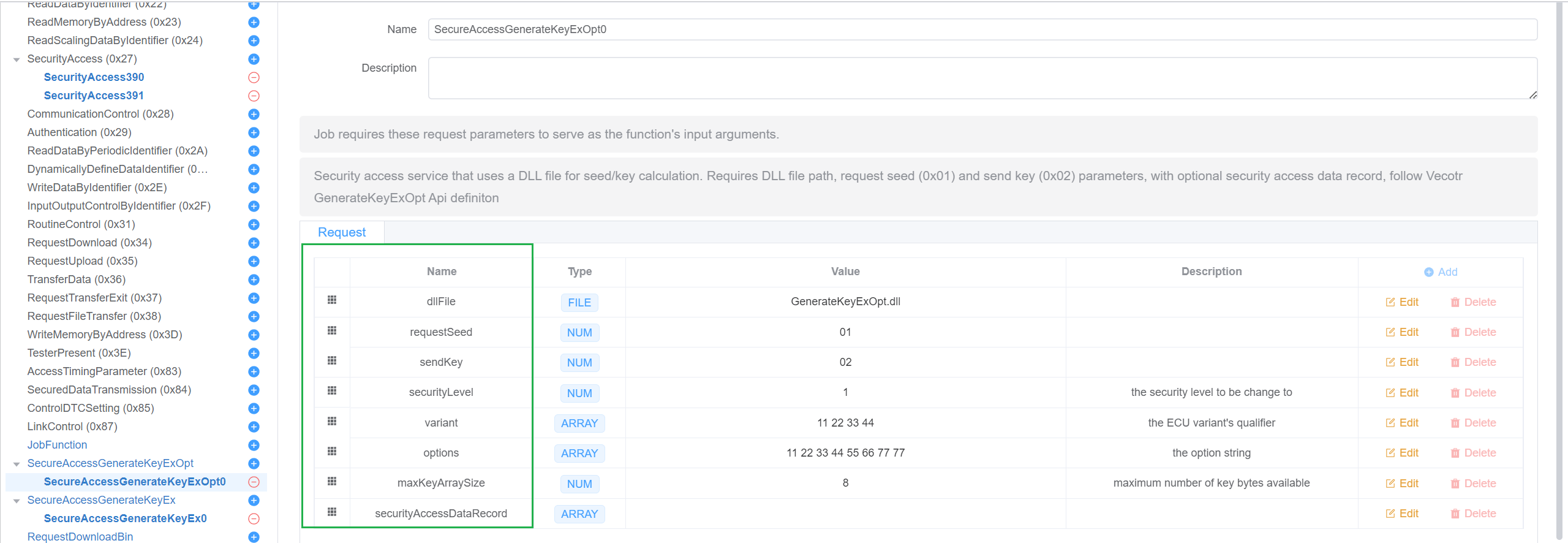
Parameters
- dllFile
- The path to the DLL file, the DLL must be a 64-bit DLL file and contains the GenerateKeyExOpt function.
VKeyGenResultExOpt GenerateKeyExOpt (
const unsigned char* ipSeedArray,
unsigned int iSeedArraySize,
const unsigned int iSecurityLevel,
const char* ipVariant,
const char* ipOptions,
unsigned char* iopKeyArray,
unsigned int iMaxKeyArraySize,
unsigned int& oActualKeyArraySize
);requestSeed
- The request seed sub-function, 1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15
- Default: 0x01
sendKey
- The send key sub-function, 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16
- Default: 0x02
securityLevel
- The security level to be change to
variant
- The variant of the security access process
options
- The options of the security access process
maxKeyArraySize
- The max key array size
securityAccessDataRecord
- The security access data record in request seed DiagRequest, the data will be sent to the ECU in the request seed sub-function.
RequestDownloadBin
A combined service that handles the complete binary download process by orchestrating UDS services 0x34 (RequestDownload), 0x36 (TransferData), and 0x37 (TransferExit).
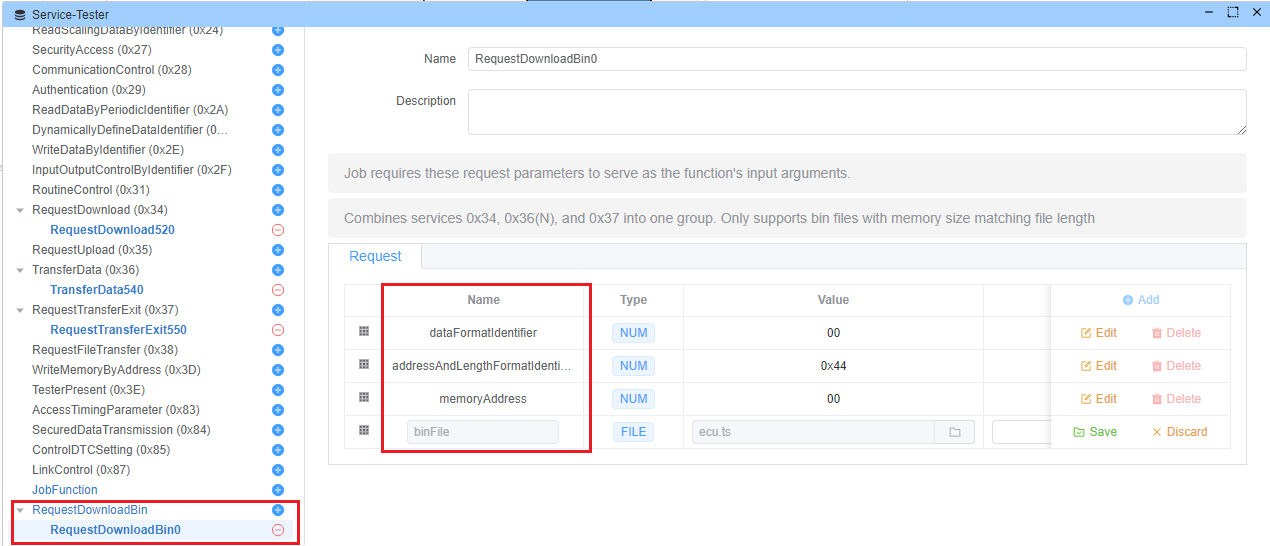
Description
This script automates the process of downloading binary files to an ECU by:
- Initiating the download request
- Transferring the data in appropriate chunks
- Completing the transfer process
Parameters
dataFormatIdentifier (8-bit)
- Format identifier for the data to be transferred
- Default: 0x00
addressAndLengthFormatIdentifier (8-bit)
- Specifies the format of memory address and length
- Default: 0x44 (4 bytes for address, 4 bytes for length)
memoryAddress (depends on addressAndLengthFormatIdentifier)
- Target memory address for the download
- Default: 0x00000000
binFile
- Binary file to be downloaded, will change memory size automatically
Creating Custom Scripts
Custom scripts can be created to extend the functionality of the diagnostic system. Your can create and save your own script, and use it in the future.
Here's how to create your own script:
Script Structure
Directory Setup
- Create a new directory under
${App Install Path}/resources/app.asar.unpacked/resources/buildInScript/ - Name it according to your script's function (e.g.,
MyCustomScript)
- Create a new directory under
Required Files
plugin.json: Configuration fileindex.js: Implementation file
plugin.json Configuration
{
"service": {
"name": "MyCustomScript",
"fixedParam": true,
"buildInScript": "index.js",
"hasSubFunction": false,
"desc": "Description of your script's functionality",
"defaultParams": [
{
"param": {
"id": "parameterName",
"name": "parameterName",
"bitLen": 8,
"deletable": false,
"editable": true,
"type": "NUM",
"phyValue": "00"
}
}
],
"defaultRespParams": []
}
}index.js Implementation
const ECB = require('../../lib/js');
Util.Init(() => {
const testerName = Util.getTesterName();
// Register main function
Util.Register(`${testerName}.MyCustomScript`, async function(parameters) {
// Create diagnostic requests
const request = new ECB.DiagRequest(testerName, {
id: "",
name: "",
serviceId: "0xXX", // Your service ID
params: [],
respParams: []
});
// Implement your logic here
return [request];
});
});Best Practices
Parameter Definition
- Define clear parameter structures in plugin.json
- Support appropriate data types (NUM, HEX, ASCII, BUFFER, FILE)
- Set proper bit lengths and editability
Response Processing
- Define expected response parameters
- Implement response validation
- Handle different response scenarios
Example: Simple Counter Script
// index.js
const ECB = require('../../lib/js');
Util.Init(() => {
const testerName = Util.getTesterName();
Util.Register(`${testerName}.CounterScript`, async function(startValue, increment) {
const request = new ECB.DiagRequest(testerName, {
id: "counter",
name: "Counter Service",
serviceId: "0x22",
params: [],
respParams: []
});
request.diagSetRaw(Buffer.from([startValue, increment]));
return [request];
});
});