UDS Authentication Service(0x29) Example
The 0x29 Authentication Service was introduced in ISO 14229-1:2020 as a modern replacement for the traditional Security Access (0x27) service. This guide demonstrates how to implement and test the 0x29 service using EcuBus-Pro, providing a more secure and certificate-based authentication mechanism for ECU access.
Note: ISO 15765-4 has deprecated the 0x27 service, making 0x29 the recommended approach for modern automotive security implementations.
Authentication Modes
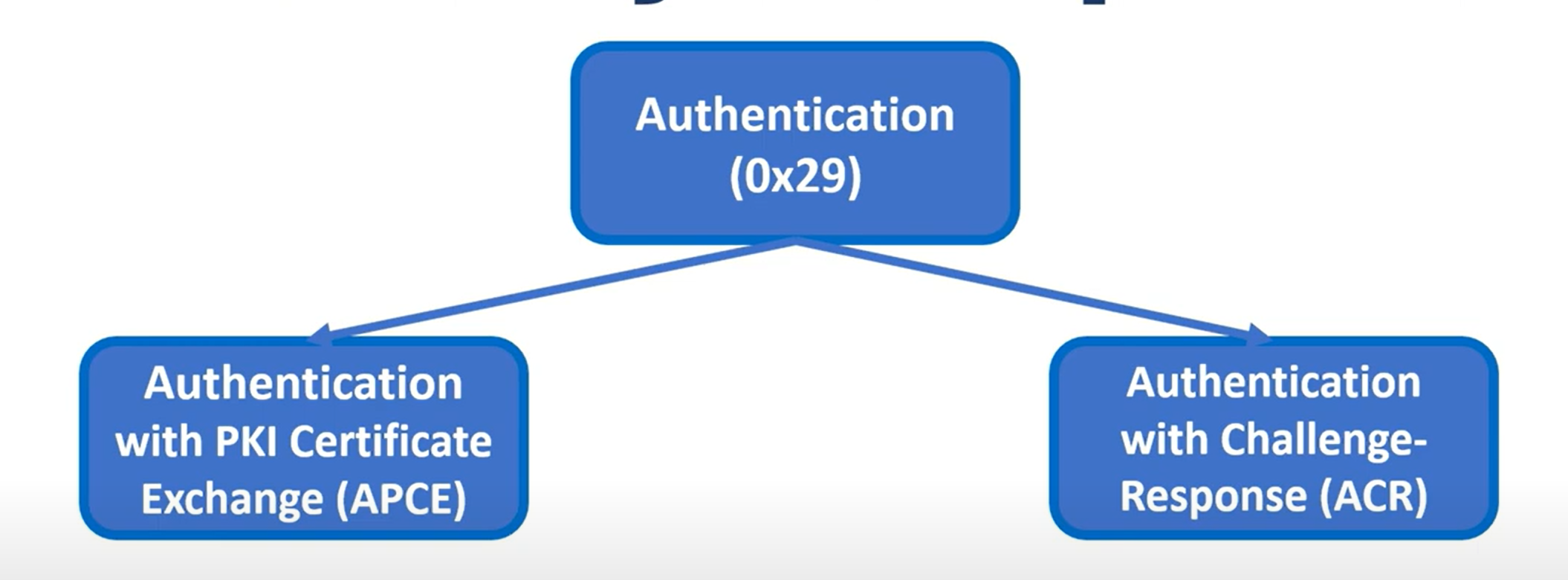
The 0x29 service supports two authentication modes:
- APCE (Asymmetric Proof of Possession and Certificate Exchange) - Primary mode
- ACR (Asymmetric Challenge Response) - Rarely used
APCE (Certificate Exchange Verification) Overview
Traditional security approaches using 0x27 had significant vulnerabilities - once a key or algorithm was compromised, any entity could access the ECU at any time. The 0x29 APCE mode addresses these issues by requiring:
- Unique Certificates: Unlike shared keys, each supplier has unique certificates containing identifying information, enabling accountability if compromised
- Certificate Authority Control: Suppliers must request certificates from OEMs, removing self-signing capabilities
- Time-Limited Access: Certificates have expiration dates, unlike permanent keys
ACR (Challenge Response) Overview
This mode is similar to 0x27 but uses asymmetric cryptography and server-generated challenges to prevent replay attacks. However, it's not widely recommended by AUTOSAR DCM.

APCE Implementation Details
The APCE authentication process uses several key sub-functions:
deAuthenticate(0x00)verifyCertificateUnidirectional(0x01)verifyCertificateBidirectional(0x02)proofOfOwnership(0x03)authenticationConfiguration(0x08)
deAuthenticate (Sub-function: 0x00)
Terminates the authentication session and resets server state.
Request Format: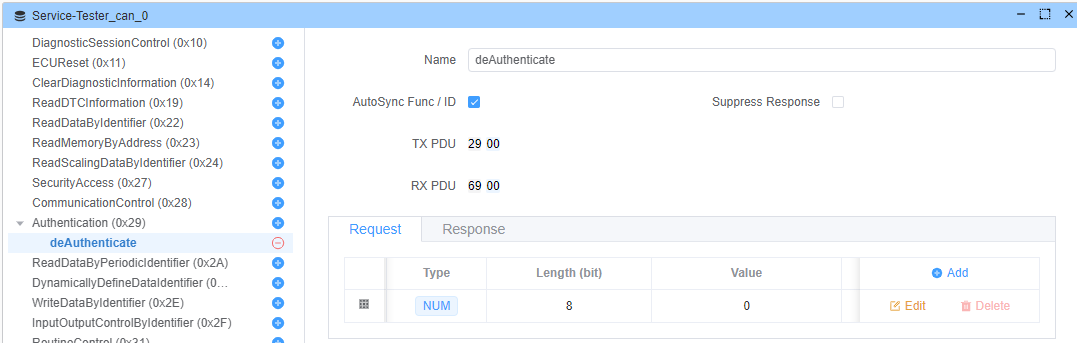
Response Format: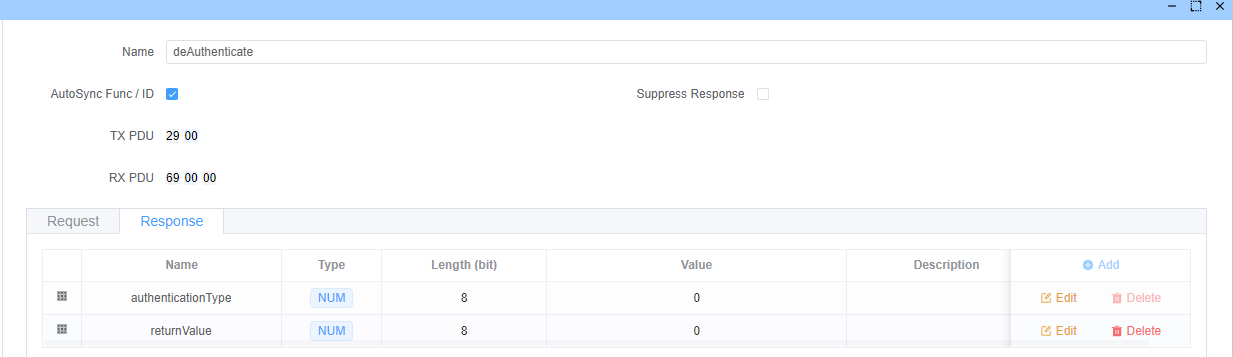
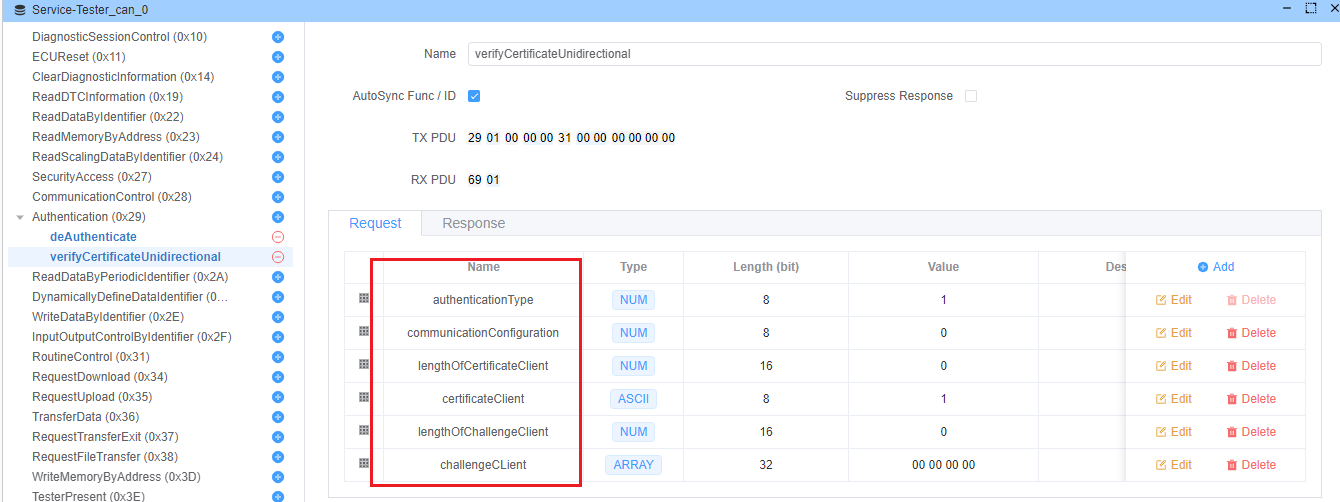
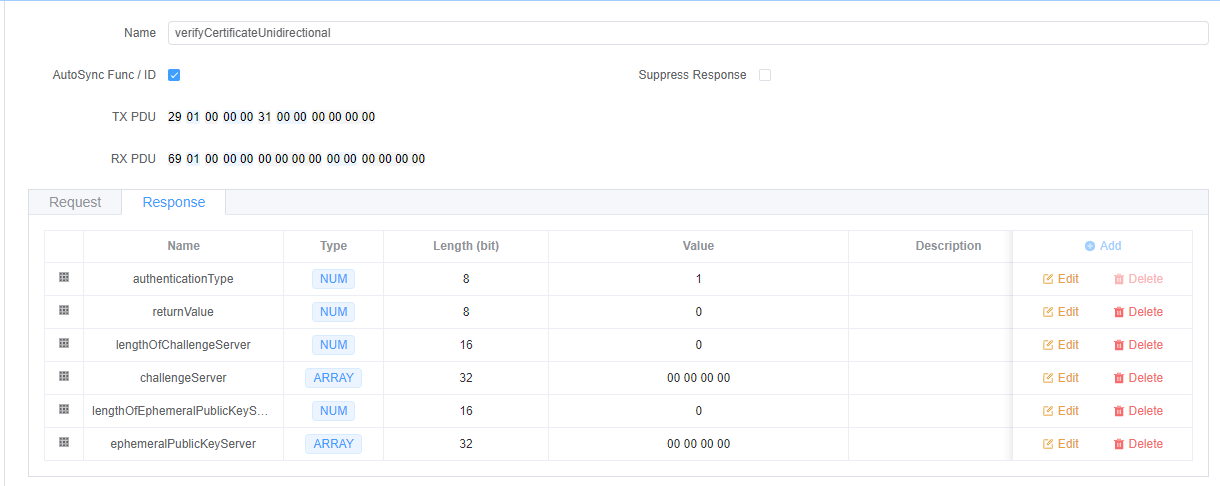
verifyCertificateUnidirectional (Sub-function: 0x01)
Initiates unidirectional certificate verification where the server validates the client.
Request Parameters:
communicationConfiguration(1 byte) - Must be 0x00lengthOfCertificateClient(2 bytes) - Certificate lengthcertificateClient(variable) - Client certificate datalengthOfChallengeClient(2 bytes) - Challenge lengthchallengeClient(variable) - Cryptographically secure random challenge
Response Parameters:
returnValue(1 byte) - Operation result codelengthOfChallengeServer(2 bytes) - Server challenge lengthchallengeServer(variable) - Server-generated challengelengthOfEphemeralPublicKeyServer(2 bytes) - Server public key lengthephemeralPublicKeyServer(variable) - Server's ephemeral ECDH/DH public key
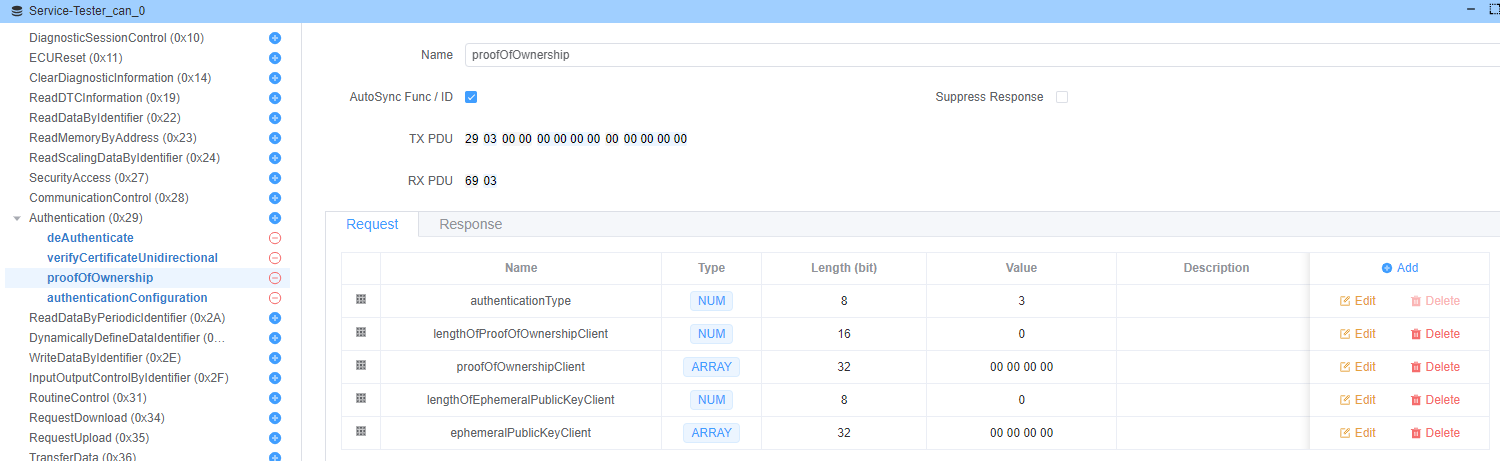
proofOfOwnership (Sub-function: 0x03)
Proves that the client possesses the private key corresponding to the certificate.
Request Parameters:
lengthOfProofOfOwnershipClient(2 bytes)proofOfOwnershipClient(variable) - Digital signature of server challengelengthOfEphemeralPublicKeyClient(2 bytes)ephemeralPublicKeyClient(variable) - Client's ephemeral public key
Verification Process: The server verifies the client's digital signature using the certificate's public key:

Response Parameters:
returnValue(1 byte) - Verification resultlengthOfSessionKeyInfo(2 bytes) - Session key information lengthsessionKeyInfo(variable) - Derived session key data

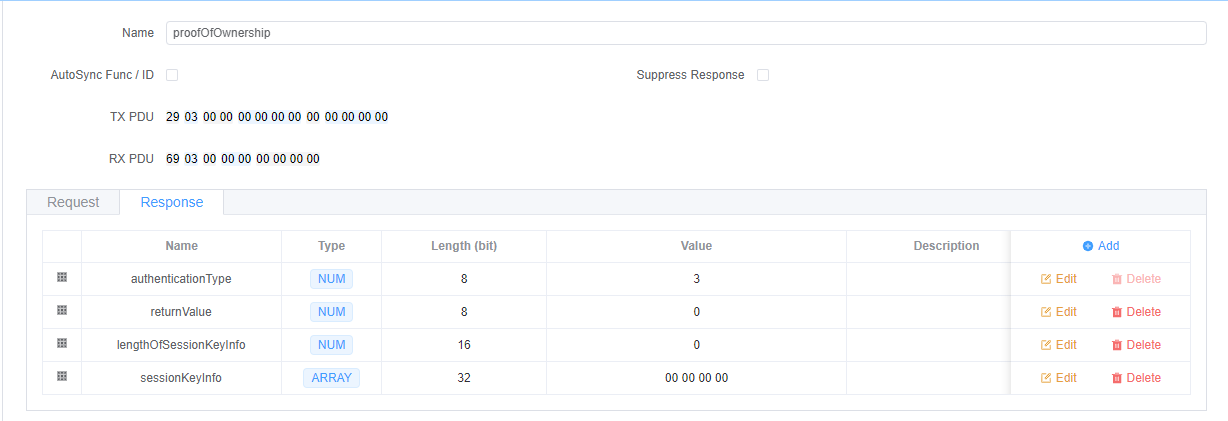
Note: AUTOSAR DCM currently does not support session keys:
authenticationConfiguration (Sub-function: 0x08)
Initiates APCE mode configuration.
Request: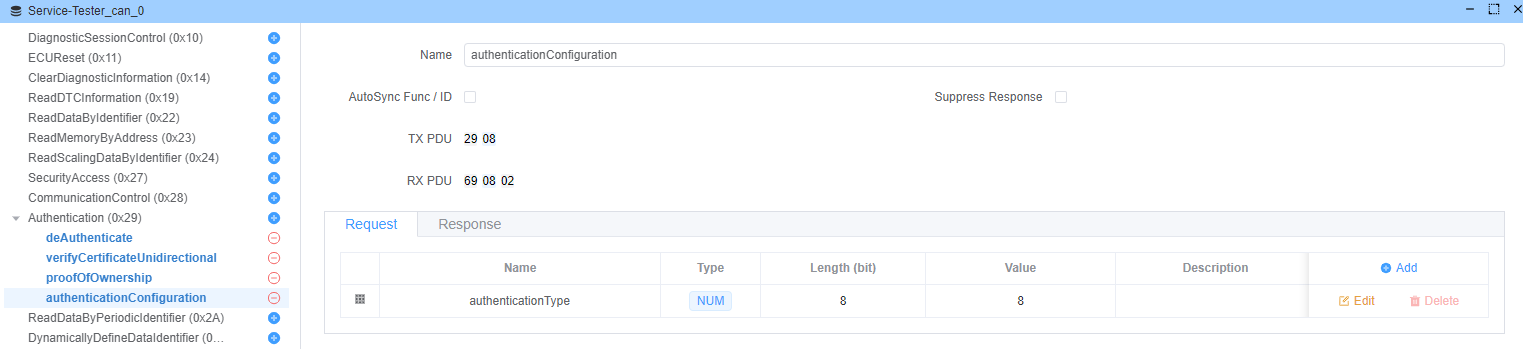
Response: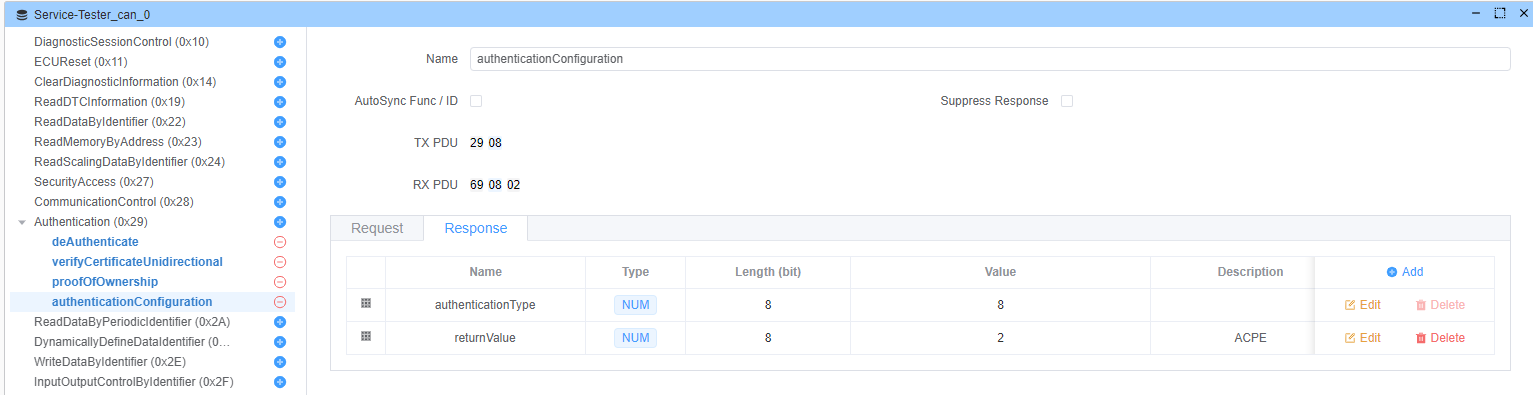
Certificate Preparation
Generate the necessary certificates using OpenSSL:
1. Generate Root CA Private Key
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 40962. Create Root CA Certificate
Create a configuration file req.cnf:
[ req ]
default_bits = 4096
prompt = no
default_md = sha256
distinguished_name = dn
x509_extensions = v3_ca
[ dn ]
C = CN
ST = ChongQing
L = ChongQing
O = EcuBus-pro
OU = EcuBus-pro Development Team
CN = app.whyengineer.com
[ v3_ca ]
basicConstraints=critical,CA:TRUEGenerate the CA certificate:
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca.key -days 400 -out ca.crt -config req.cnf
3. Generate Client Certificate
# Generate client private key
openssl genrsa -out client.key 4096
# Generate public keys
openssl rsa -in client.key -pubout > client_pub.key
openssl rsa -in ca.key -pubout > ca_pub.key
# Create certificate signing request
openssl req -new -key client.key -out client.csr -config req.cnf
# Sign the client certificate with CA
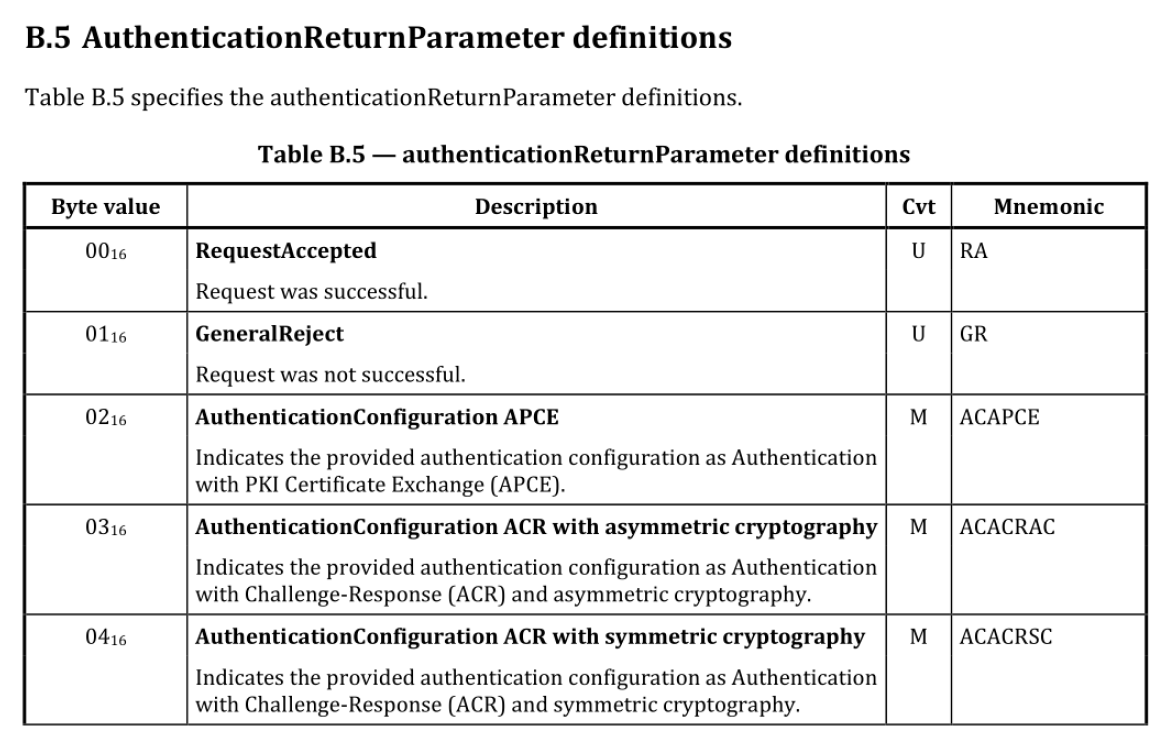
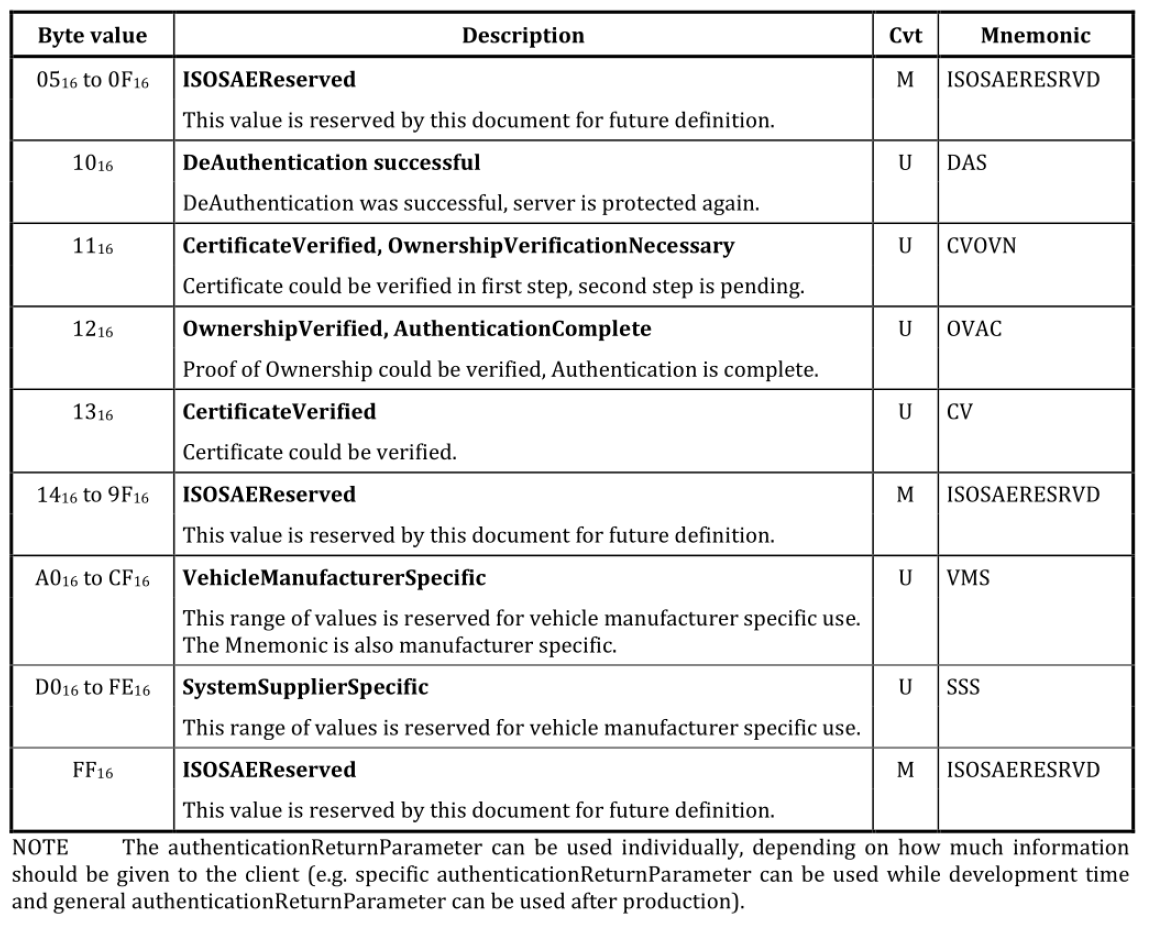
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -out client.crt -CAcreateserialReturn Value Codes
Key Exchange Algorithm (ECDH/DH)
ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman) enables two parties to establish a shared secret over an insecure channel. The algorithm works based on the property: (a × G) × b = (b × G) × a
Where:
aandbare private keysGis the generator point×represents elliptic curve point multiplication
*ECDH Process:
- Alice generates:
{alicePrivKey, alicePubKey = alicePrivKey × G} - Bob generates:
{bobPrivKey, bobPubKey = bobPrivKey × G} - They exchange public keys over insecure channel
- Alice computes: sharedKey = bobPubKey × alicePrivKey
- Bob computes: sharedKey = alicePubKey × bobPrivKey
- Both parties now have the same shared secret
Authentication Sequence
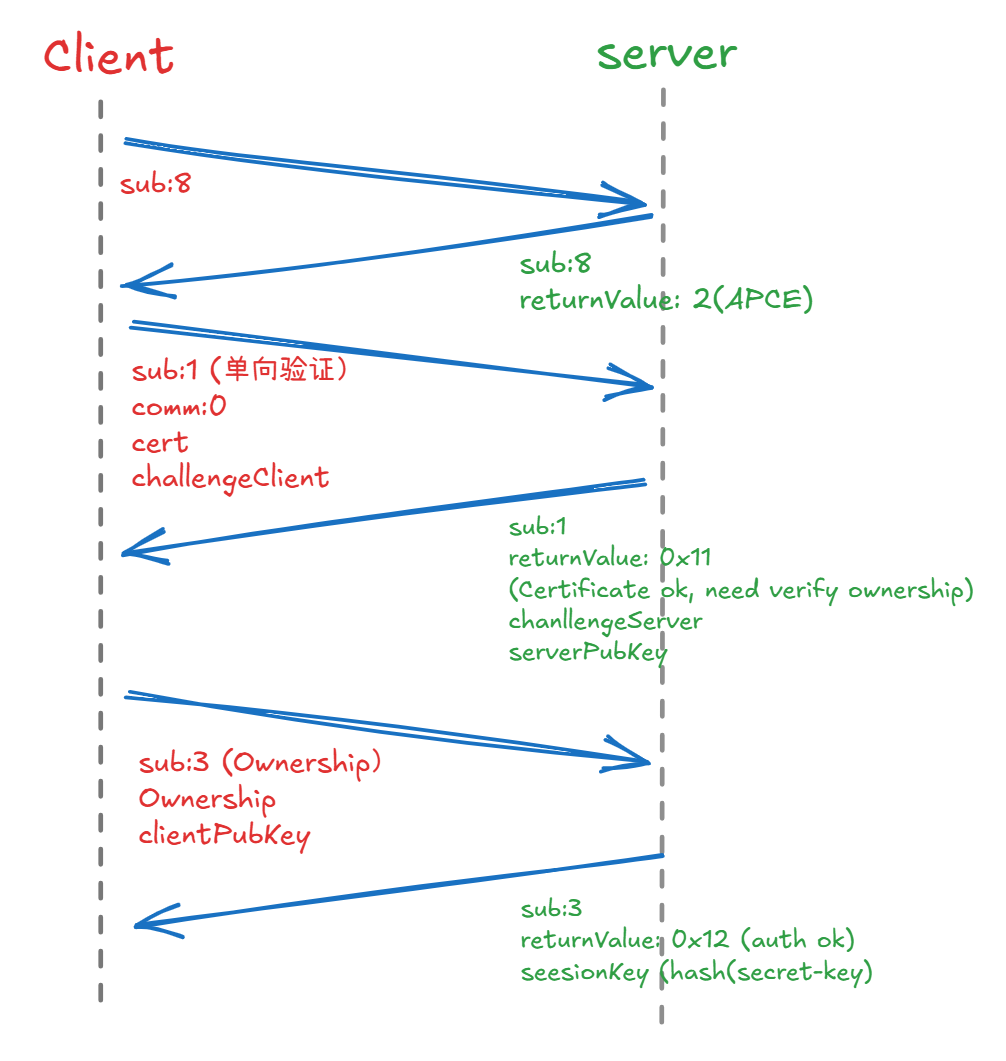
EcuBus-Pro Implementation
1. Configure Authentication Sequence
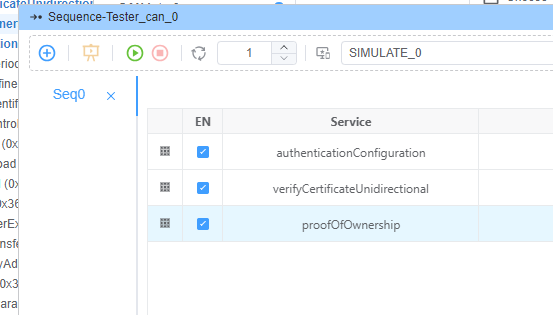
2. Configure Tester Script
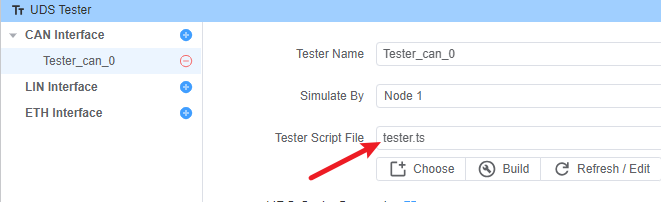
tester.ts:
import { DiagRequest } from "ECB"
import fs from 'fs/promises'
import path from "path"
const challenge = Buffer.from(Array(32).fill(0).map(() => Math.floor(Math.random() * 256)))
Util.Init(async ()=>{
// Read client certificate
const cert = await fs.readFile(path.join(process.env.PROJECT_ROOT,'client.crt'),'utf-8')
// Configure verifyCertificateUnidirectional request
const verifyCertificateUnidirectional = DiagRequest.from("Tester_can_0.verifyCertificateUnidirectional")
// Set certificate parameters
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameterSize('certificateClient',cert.length*8)
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameter('certificateClient',cert)
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameter('lengthOfCertificateClient',cert.length)
// Set challenge parameters
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameter('lengthOfChallengeClient',32)
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameterSize('challengeClient',32*8)
verifyCertificateUnidirectional.diagSetParameterRaw('challengeClient',challenge)
await verifyCertificateUnidirectional.changeService()
})3. Configure ECU Simulator
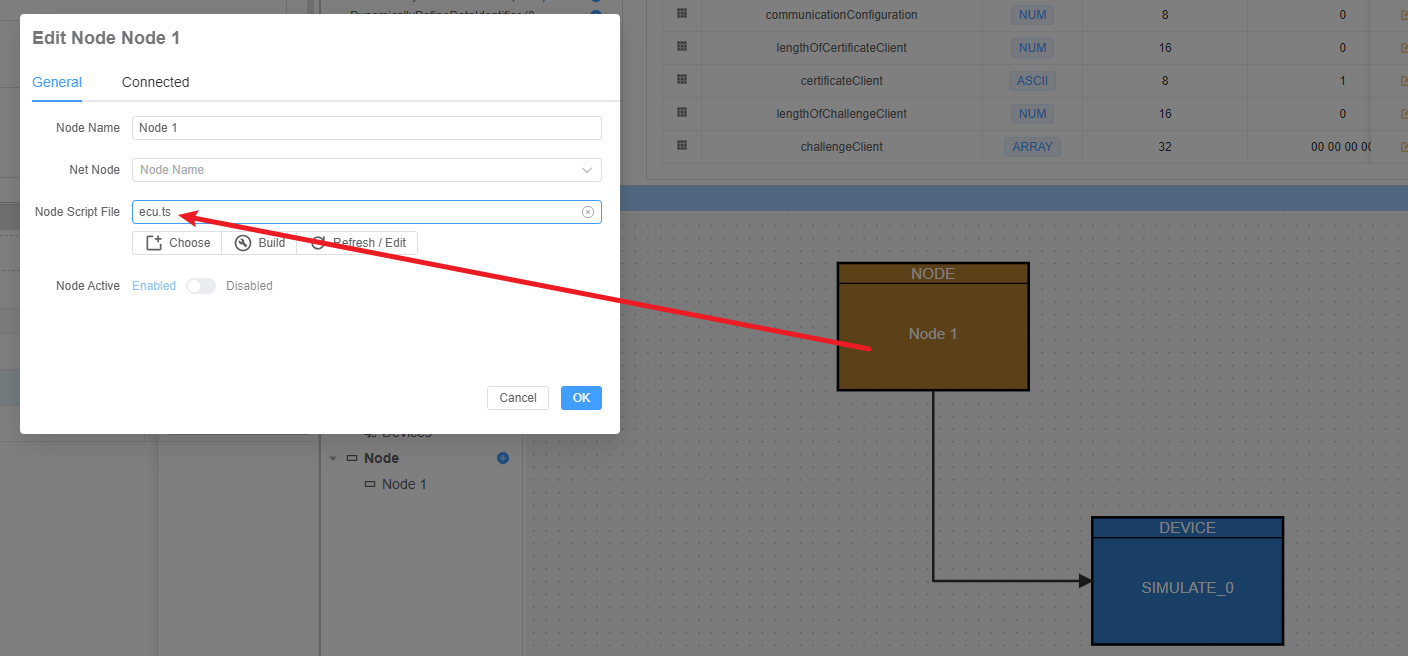
ecu.ts:
import { DiagResponse } from "ECB"
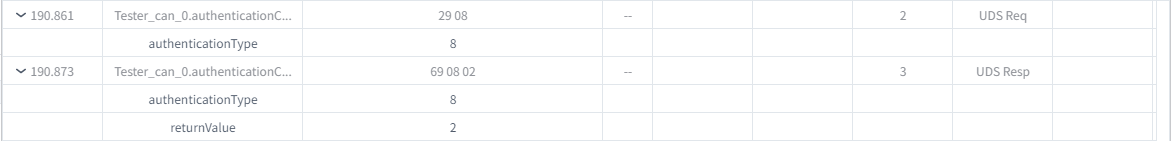
Util.On("Tester_can_0.authenticationConfiguration.send",async (req)=>{
const resp=DiagResponse.fromDiagRequest(req)
resp.diagSetParameterSize('returnValue',0x2) // APCE mode
await resp.outputDiag()
})
4. Certificate Verification Process
Util.On("Tester_can_0.verifyCertificateUnidirectional.send",async (req)=>{
const resp=DiagResponse.fromDiagRequest(req)
const data=req.diagGetRaw()
const lengthOfCertificateClient=data.readUint16BE(3)
console.log(`Certificate length: ${lengthOfCertificateClient}`)
// Parse and verify certificate
const cert=new crypto.X509Certificate(data.subarray(5,5+lengthOfCertificateClient))
console.log(`Certificate issuer: ${cert.issuer}`)
const ca_str= await fs.readFile(path.join(process.env.PROJECT_ROOT,'ca.crt'),'utf-8')
const ca=new crypto.X509Certificate(ca_str)
const verifyResult=cert.verify(ca.publicKey)
console.log(`Verification result: ${verifyResult}`)
if(verifyResult){
resp.diagSetParameter('lengthOfChallengeServer',32)
resp.diagSetParameterSize('challengeServer',32*8)
resp.diagSetParameterRaw('challengeServer',challenge)
resp.diagSetParameter('returnValue',0x11) // Certificate OK, verify ownership
await resp.outputDiag()
} else {
throw new Error('Client certificate verification failed')
}
})

5. Digital Signature Process
Util.On("Tester_can_0.verifyCertificateUnidirectional.recv",async (resp)=>{
const data=resp.diagGetRaw()
const lengthOfChallengeServer=data.readUint16BE(3)
const challenge=data.subarray(5,5+lengthOfChallengeServer)
console.log(`Challenge: ${challenge.toString('hex')}`)
// Sign challenge with client private key
const privateKey=await fs.readFile(path.join(process.env.PROJECT_ROOT,'client.key'),'utf-8')
const sign=crypto.sign('RSA-SHA256',challenge,privateKey)
console.log(`Signature: ${sign.toString('hex')}`)
// Configure proof of ownership request
const proofOfOwnership = DiagRequest.from("Tester_can_0.proofOfOwnership")
proofOfOwnership.diagSetParameterSize('proofOfOwnershipClient',sign.length*8)
proofOfOwnership.diagSetParameterRaw('proofOfOwnershipClient',sign)
proofOfOwnership.diagSetParameter('lengthOfProofOfOwnershipClient',sign.length)
await proofOfOwnership.changeService()
})
6. Ownership Verification
First, extract the public key from the certificate:
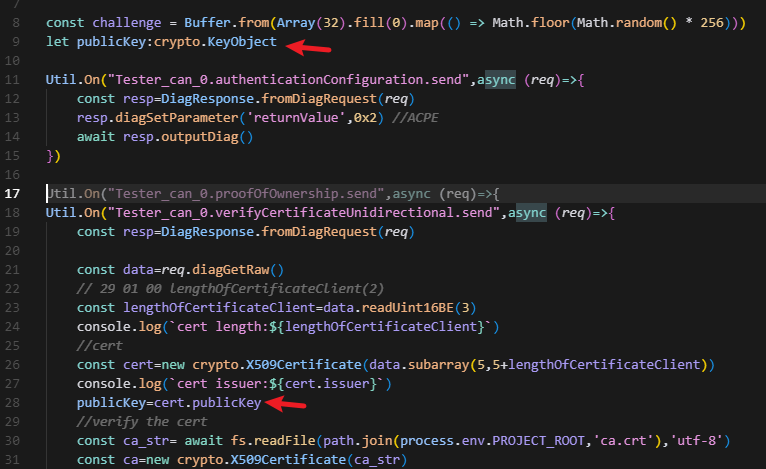
Then verify the signature:
Util.On("Tester_can_0.proofOfOwnership.send",async (req)=>{
const resp=DiagResponse.fromDiagRequest(req)
const data=req.diagGetRaw()
const lengthOfProofOfOwnershipClient=data.readUint16BE(2)
const sign=data.subarray(4,4+lengthOfProofOfOwnershipClient)
// Verify signature using certificate's public key
const verifyResult=crypto.verify('RSA-SHA256',challenge,publicKey,sign)
console.log(`Verification result: ${verifyResult}`)
if(verifyResult){
resp.diagSetParameter('returnValue',0x12) // Authentication successful
await resp.outputDiag()
} else {
throw new Error('Client signature verification failed')
}
})
