CAN High-Precision Timer Example
NOTE
This example requires a CAN device with hardware timestamp capability to measure the time intervals between received CAN messages. This demo uses a KVASER USB-to-CAN device.
Overview
This example demonstrates how to measure the time intervals between consecutive CAN messages using hardware timestamps. The hardware timestamp provides microsecond-level precision, allowing accurate measurement of message intervals.
Code Example
typescript
import { setVar } from 'ECB'
let t1: number | undefined
Util.OnCan(1, (msg) => {
const t = msg.ts
if (!t1) {
t1 = t
} else {
const diff = (t - t1) / 1000
setVar('DIFF', diff)
t1 = t
}
})How It Works
- The code listens to CAN messages on channel 1 using
Util.OnCan - For each received message, it extracts the hardware timestamp (
msg.ts) in microseconds - It calculates the time difference between consecutive messages
- The difference is converted to milliseconds and stored in the
DIFFvariable
Results
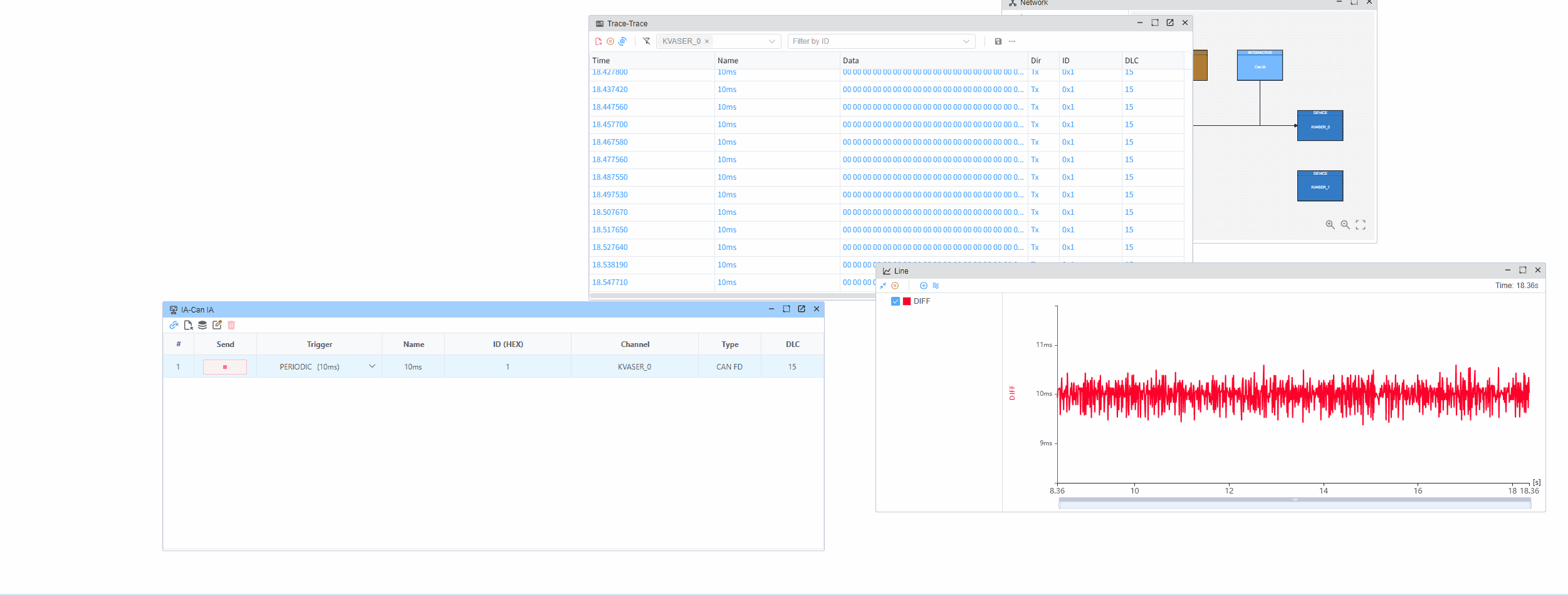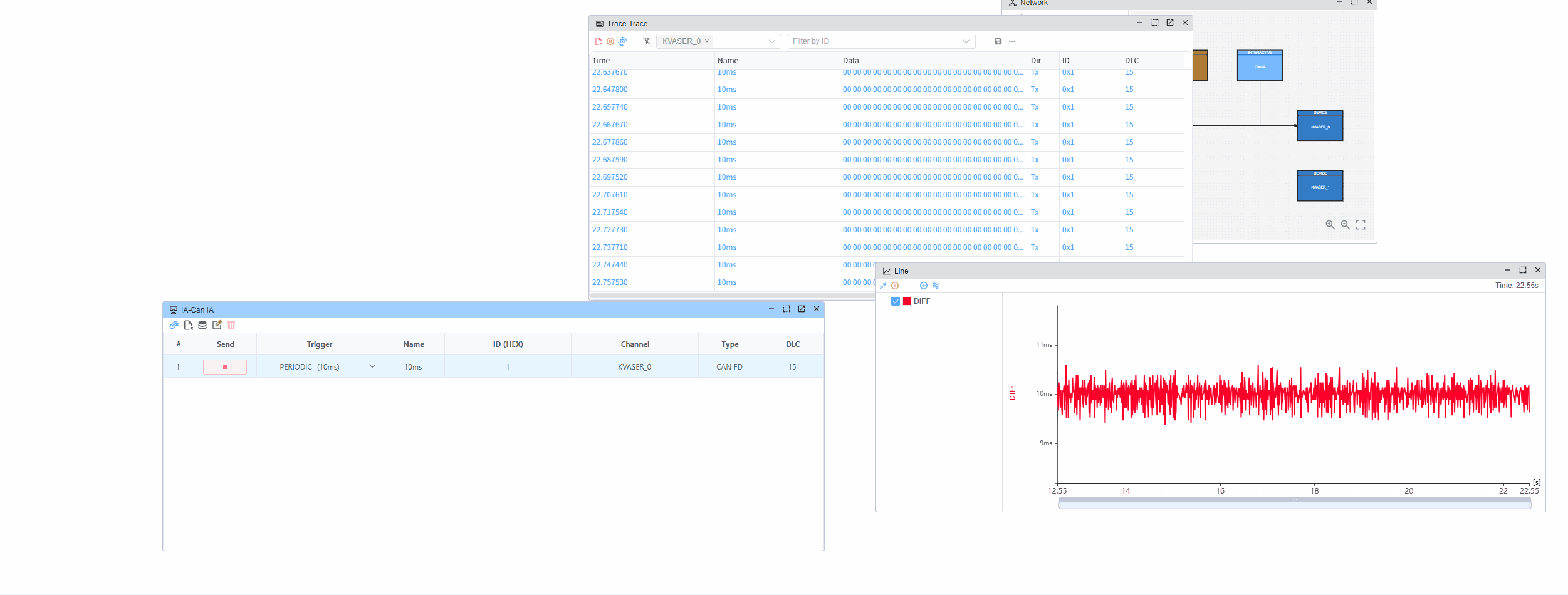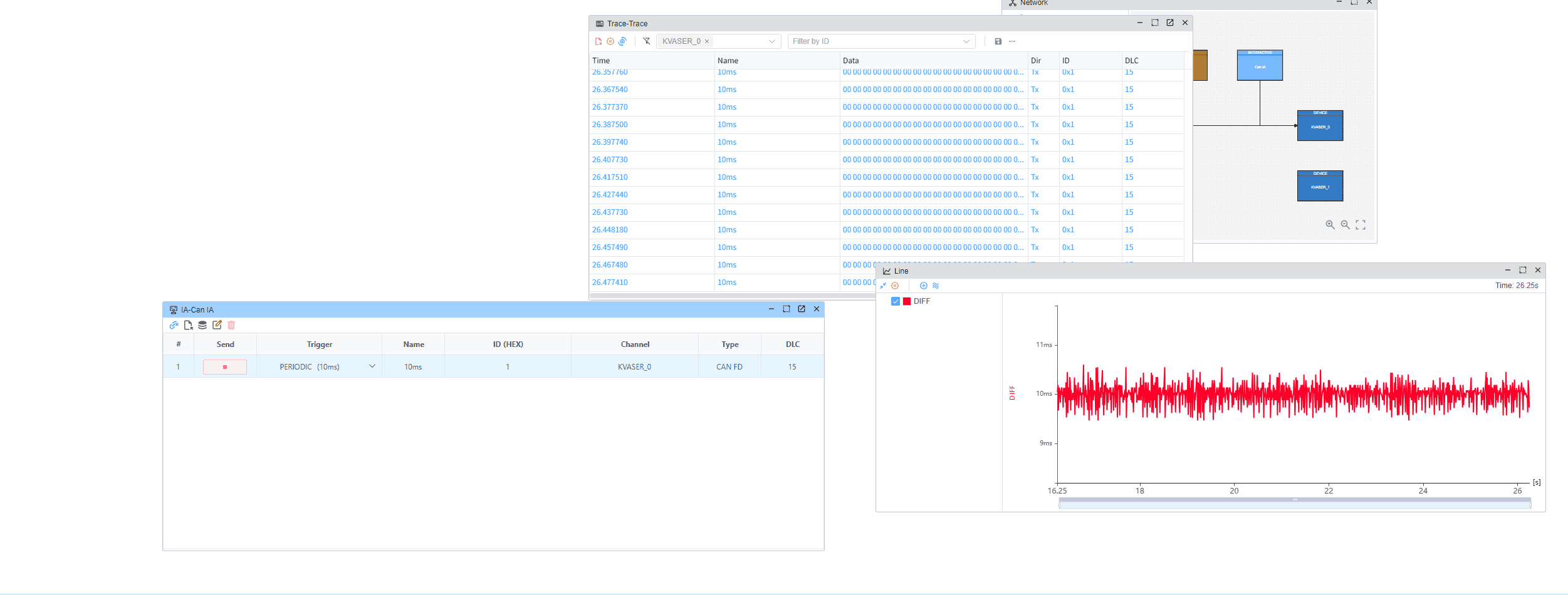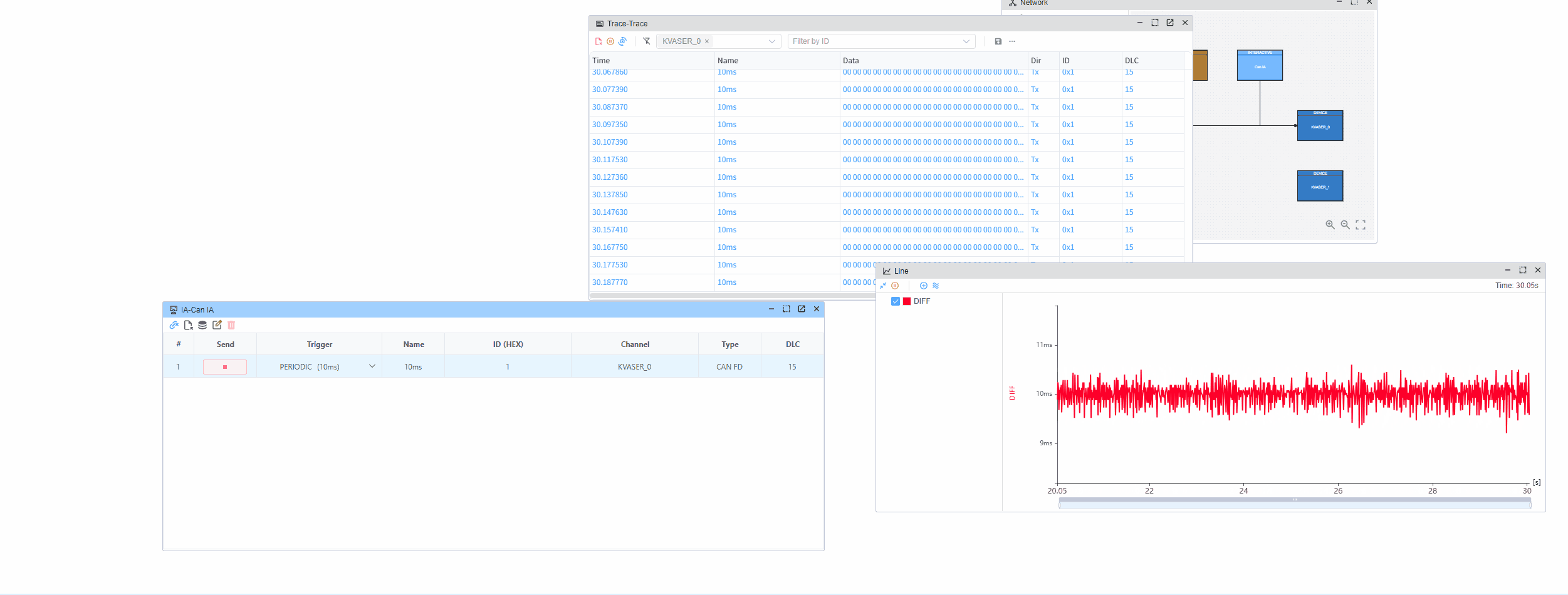
Through hardware timestamps, you can accurately measure the time intervals between received CAN messages with microsecond-level precision.