NXP Bootloader Example
- Interface:
CAN - Vendor Device: KVASER Leaf V3
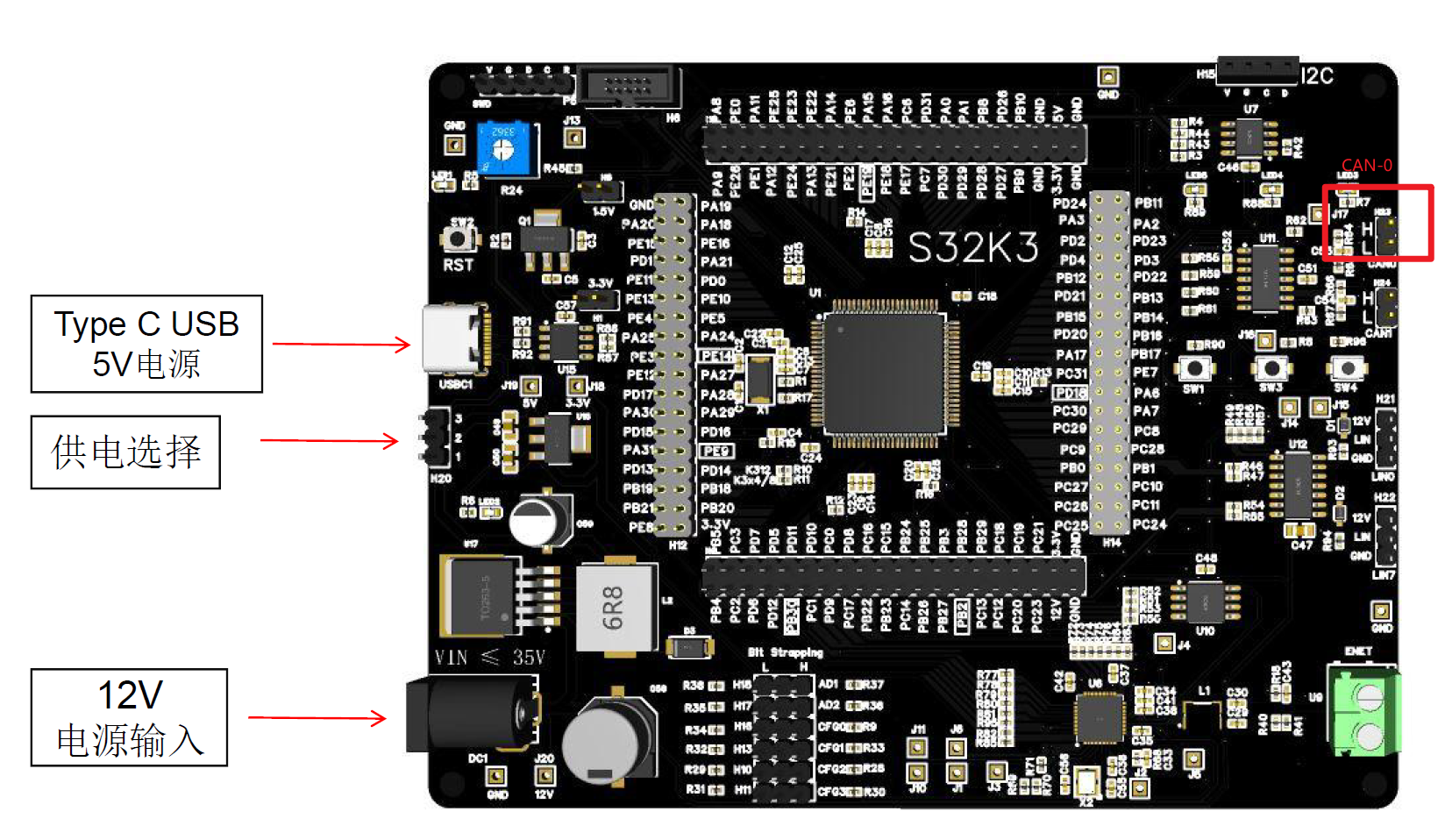
- Test Board: S32K344/324/314大开发板EVB评估板, or NXP S32K344EVB.
- Ecu Code: NXP Bootloader
Description
This example demonstrates how to use the EcuBus-Pro to upgrade Application firmware through UDS CAN protocol. This example use KVASER Leaf V3 as USB-CAN adapter.
CAN Configuration
- CAN
- Baudrate: 500Kbps
- TX ID: 0x784
- RX ID: 0x7f0
Connection
| KVASER Leaf V3 | S32K344大开发板EVB评估板 |
|---|---|
| CANH | CAN0 H23-1 |
| CANL | CAN0 H23-2 |
Usage
- Download the NXP Bootloader.
- The download demo is based on old EcuBus tool, which is deprecated. The new EcuBus-Pro tool has more features and better performance.
- If you use the
NXP S32K344EVB, you can directly download the firmware. If you use theS32K344大开发板EVB评估板, you need to modify the LPUART pins and LED pins. - Connect the USB-CAN adapter to the computer, and connect the
KVASER Leaf V3USB-CAN adapter to the S32K344 board. - Run the Sequence-Tester_1.
Diagnostic Steps

This example implements firmware upgrade through UDS diagnostic protocol. The main steps are as follows:
Session Control and Communication Control
- DiagnosticSessionControl (0x10) switch to programming session (0x03)
- CommunicationControl (0x28) disable normal communication (controlType=0x03)
- DiagnosticSessionControl (0x10) switch to extended session (0x02)
Security Access
- SecurityAccess (0x27, subfunction=0x01) request seed
- SecurityAccess (0x27, subfunction=0x02) send key
- Key calculation uses AES-128-CBC algorithm, key is [0-15], IV is all zeros
Write Identifier
- WriteDataByIdentifier (0x2E, DID=0xF15A) write specific identifier
Download Program For each firmware file:
- RequestDownload (0x34) request download, specify memory address and size
- RoutineControl (0x31, routineId=0x0202) verify CRC
- TransferData (0x36) transfer data in blocks
- RequestTransferExit (0x37) end transfer
Firmware Verification and Reset
- RoutineControl (0x31, routineId=0xFF00) verify firmware
- RoutineControl (0x31, routineId=0xFF01) verification complete
- ECUReset (0x11) reset ECU
Firmware Files
The example includes two firmware files:
S32K344_FlsDrvRTD100.bin
- Download Address: 0x20000010
- Driver firmware
S32K344_CAN_App_RTD200.bin
- Download Address: 0x00440200
- Application firmware
Notes
- Ensure firmware files are placed in the project's bin directory
- Do not disconnect or power off during download
- If download fails, you can retry the entire process
- Each firmware file needs CRC verification
Script Implementation Details
The bootloader.ts script implements the diagnostic sequence. Here's a detailed explanation of each part:
Initialization and Imports
typescript
import crypto from 'crypto'
import { CRC, DiagRequest, DiagResponse } from 'ECB'
import path from 'path'
import fs from 'fs/promises'- Imports required modules for cryptography, CRC calculation, and file operations
ECBprovides UDS diagnostic communication utilities
Configuration
typescript
const crc = new CRC('self', 16, 0x3d65, 0, 0xffff, true, true)
let maxChunkSize: number | undefined = undefined
let content: undefined | Buffer = undefined- Configures CRC-16 calculator for firmware verification
- Variables to store transfer block size and firmware content
Firmware Files Configuration
typescript
const fileList = [
{
addr: 0x20000010,
file: path.join(process.env.PROJECT_ROOT, 'bin', 'S32K344_FlsDrvRTD100.bin')
},
{
addr: 0x00440200,
file: path.join(process.env.PROJECT_ROOT, 'bin', 'S32K344_CAN_App_RTD200.bin')
}
]- Defines firmware files to be downloaded with their target addresses
Initialization Handler
typescript
Util.Init(async () => {
const req = DiagRequest.from('Tester_1.RoutineControl491')
req.diagSetParameter('routineControlType', 1)
await req.changeService()
const resp = DiagResponse.from('Tester_1.RoutineControl491')
resp.diagSetParameter('routineControlType', 1)
await resp.changeService()
})- Modifies RoutineControl491 service to use type 1 (start routine)
- Updates both request and response parameters
Security Access Handler
typescript
Util.On('Tester_1.SecurityAccess390.recv', async (v) => {
const data = v.diagGetParameterRaw('securitySeed')
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(
'aes-128-cbc',
Buffer.from([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]),
Buffer.alloc(16, 0)
)
let encrypted = cipher.update(data)
cipher.final()
const req = DiagRequest.from('Tester_1.SecurityAccess391')
req.diagSetParameterSize('data', 128)
req.diagSetParameterRaw('data', encrypted)
await req.changeService()
})- Handles security access seed-key exchange
- Uses AES-128-CBC to calculate key from received seed
- Sends calculated key back to ECU
Download Process Handlers
typescript
Util.Register('Tester_1.JobFunction0', async () => {
// Prepare next firmware file for download
const item = fileList.shift()
if (item) {
// Request download and verify CRC
// Returns array of requests to be sent
}
return []
})
Util.Register('Tester_1.JobFunction1', () => {
// Handle actual data transfer
// Splits firmware into chunks and sends them
// Ends with transfer exit request
// Returns array of requests to be sent
})- JobFunction0: Prepares download by:
- Getting next firmware file
- Setting up download request with correct address
- Calculating and verifying CRC
- JobFunction1: Handles data transfer by:
- Splitting firmware into appropriate chunk sizes
- Creating TransferData requests for each chunk
- Adding RequestTransferExit at the end
- Triggering firmware verification after last file
The script works in conjunction with the sequence defined in the ECB file, which executes:
- Session and communication control services
- Security access sequence
- JobFunction0 to prepare download
- JobFunction1 to transfer data
- Final verification and reset