DoIP Gateway
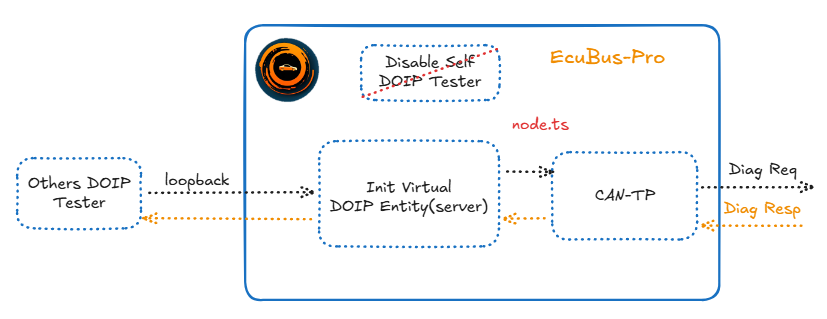
This example demonstrates how to implement a DoIP to CAN gateway that bridges communication between DoIP testers and CAN-based ECUs. The gateway receives DoIP diagnostic requests and forwards them to CAN bus, then returns the CAN responses back via DoIP.
Architecture Overview
The example simulates a DoIP gateway that:
- Registers as a DoIP virtual entity - see the example for details on virtual entity registration
- Receives DoIP diagnostic requests from Ethernet testers
- Forwards requests to CAN bus via CANTP
- Returns CAN responses back to the DoIP tester
Setup
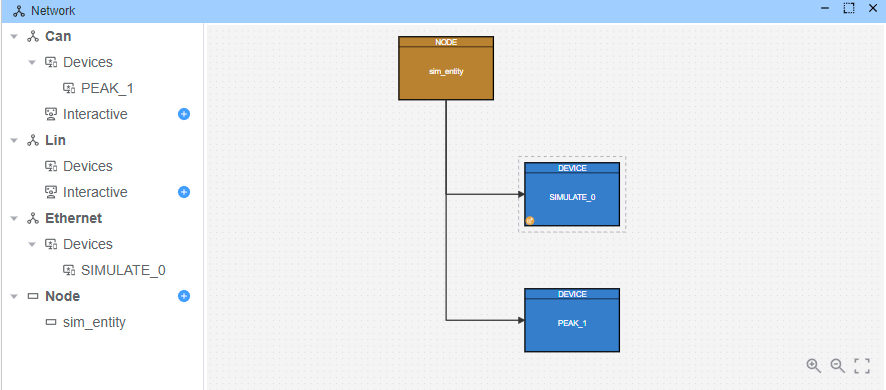
Device Configuration
Configure the network topology with:
- Eth: Ethernet connection for DoIP communication
- Can: CAN bus connection for ECU communication
- Devices:
SIMULATE_0: Simulates the DoIP interfacePEAK_1: CAN interface for ECU communication
Node Configuration
Add a node item and attach the gateway script (node.ts)
The gateway script implements the following functionality:
typescript
import { DiagResponse, output, RegisterEthVirtualEntity } from 'ECB'
Util.Init(async () => {
console.log('Registering virtual entity')
await RegisterEthVirtualEntity(
{
vin: '123456789',
eid: '00-00-00-00-00-00',
gid: '00-00-00-00-00-00',
logicalAddr: 100
},
'127.0.0.1'
)
})
Util.On("Tester_eth_1.*.send", async (req) => {
console.log('Received DOIP Diag request')
req.testerName='Tester_can_0'
await req.outputDiag('PEAK_1')
})
Util.On("Tester_can_0.*.recv", async (resp) => {
console.log('Received CANTP Diag response')
resp.testerName='Tester_eth_1'
await resp.outputDiag('SIMULATE_0')
})Key Features:
- DoIP Entity Registration: Registers a virtual entity with logical address 100
- Request Forwarding: Converts DoIP requests to CAN diagnostic requests
- Response Bridging: Forwards CAN responses back to DoIP tester
Using Python Client As Other Tester
A Python test client (client.py) is provided for external testing:
python
import udsoncan
from doipclient import DoIPClient
from doipclient.connectors import DoIPClientUDSConnector
from udsoncan.client import Client
from udsoncan.services import *
udsoncan.setup_logging()
ecu_ip = '127.0.0.1'
ecu_logical_address = 100
doip_client = DoIPClient(ecu_ip, ecu_logical_address, client_logical_address=200)
conn = DoIPClientUDSConnector(doip_client)
with Client(conn, request_timeout=2) as client:
try:
client.change_session(DiagnosticSessionControl.Session.extendedDiagnosticSession)
except NegativeResponseException as e:
print('Server refused request:', e.response.code_name)
except (InvalidResponseException, UnexpectedResponseException) as e:
print('Invalid server response:', e.response.original_payload)
doip_client.close()Prerequisites for Python client:
bash
pip install udsoncan doipclientExecution
- Start the simulation: Start Run in EcuBus-Pro
- Monitor traffic: Use the built-in trace window to view all frames
- Alternative monitoring: Use Wireshark to capture network traffic
- Test with Python: Run
python client.pyto send test requests