E2E (End-to-End) Protection
Overview
E2E (End-to-End) protection is a safety mechanism used in automotive systems to detect message corruption, loss, or replay attacks. This feature allows you to implement E2E protection for CAN messages by intercepting messages before transmission and adding checksums and sequence counters.
NOTE
Currently, E2E protection is only supported for CAN bus messages.
Background
Sometimes it is necessary to perform modifications to the calculated checksum and counters before the CAN message is sent out. Possible reasons could be:
- Special Fault Injection use cases
- Custom E2E protection schemes that differ from standard implementations
The setTxPending callback allows users to modify a message's payload just before it is actually sent. The bytes of the message's payload can be read and also be overwritten. This enables you to:
- Add sequence counters to track message order
- Calculate and insert checksums (CRC) based on the message data
- Perform fault injection by modifying checksums or counters
- Implement custom E2E protection algorithms
How It Works
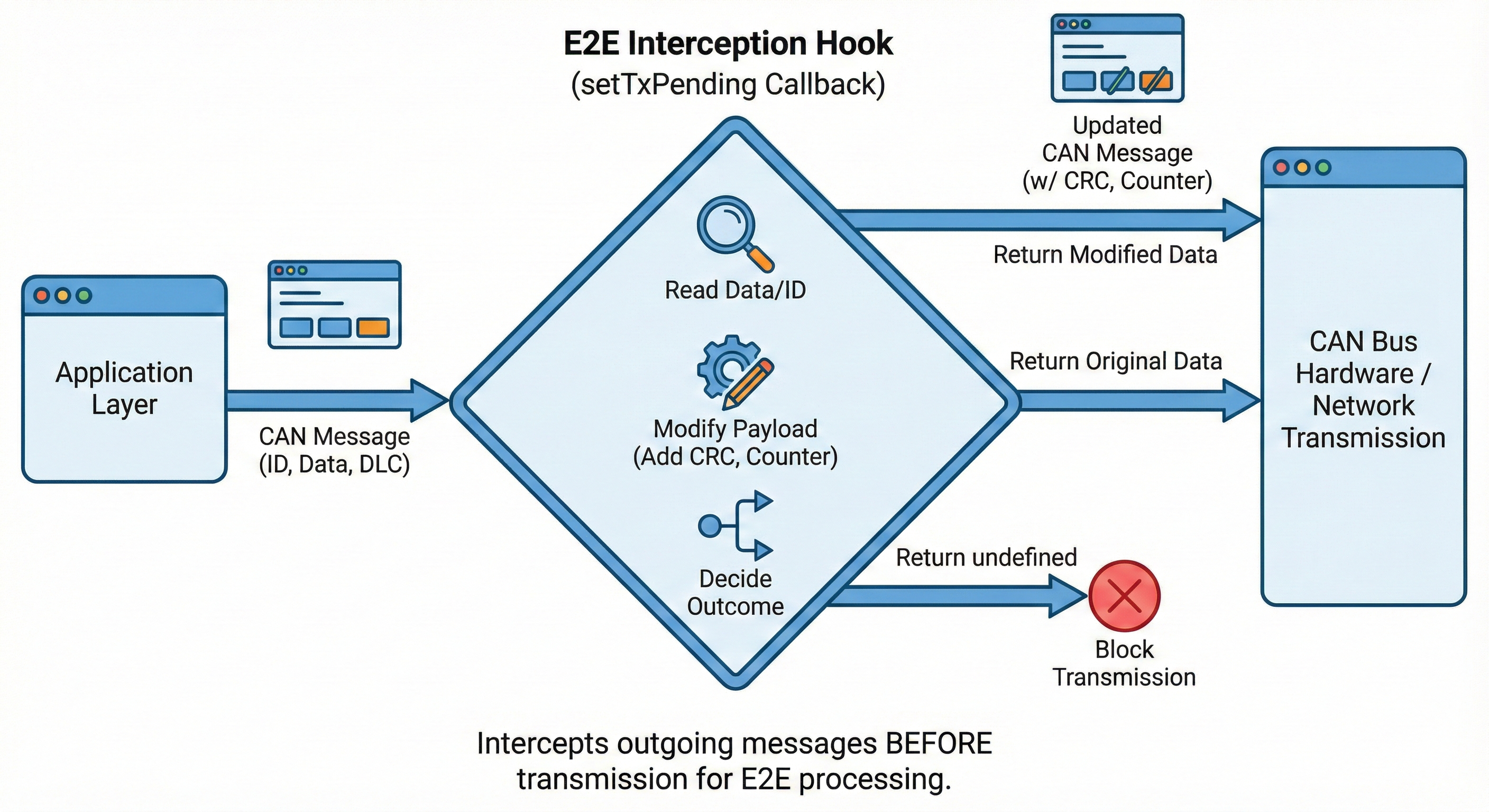
The setTxPending function registers a callback that intercepts all outgoing messages before transmission. The callback receives a [CanMessage] object and can:
- Read the message data (including any pre-calculated checksums or counters)
- Modify the message data (update counters, calculate checksums, etc.)
- Return the modified data buffer to send the message
- Return
undefinedto suppress/block the transmission - Return the original
msg.datato send the message unchanged
Basic Usage
The following example demonstrates a basic E2E protection scheme where:
- Byte 6: Contains a sequence counter (0-255, wraps around)
- Byte 7: Contains a CRC8 checksum computed over bytes 0-6
import { CRC, setTxPending } from 'ECB'
let cnt = 0
const crc8 = CRC.buildInCrc('CRC8')!
setTxPending((msg) => {
if (msg.id === 1 && msg.data.length === 8) {
// Update sequence counter in byte 6
msg.data[6] = (cnt++) % 256
// Calculate CRC8 over bytes 0-6 (excluding the checksum byte)
msg.data[7] = crc8.compute(msg.data.subarray(0, 7))
return msg.data
} else {
// For other messages, send unchanged
return msg.data
}
})Blocking Message Transmission
You can prevent a message from being sent by returning undefined:
import { setTxPending } from 'ECB'
setTxPending((msg) => {
// Block transmission of messages with ID 0x100
if (msg.id === 0x100) {
return undefined // Message will not be sent
}
return msg.data // Other messages sent normally
})Important Notes
Performance: The callback is called for every outgoing CAN message. Keep the callback logic efficient to avoid impacting message transmission timing.
E2E Profile Compatibility: The built-in CRC algorithms correspond to common E2E profiles, but for full AUTOSAR E2E profile compliance, you may need to implement additional steps beyond simple CRC calculation (e.g., data ID inclusion, counter handling). Refer to the corresponding AUTOSAR specifications for complete E2E profile implementation details.